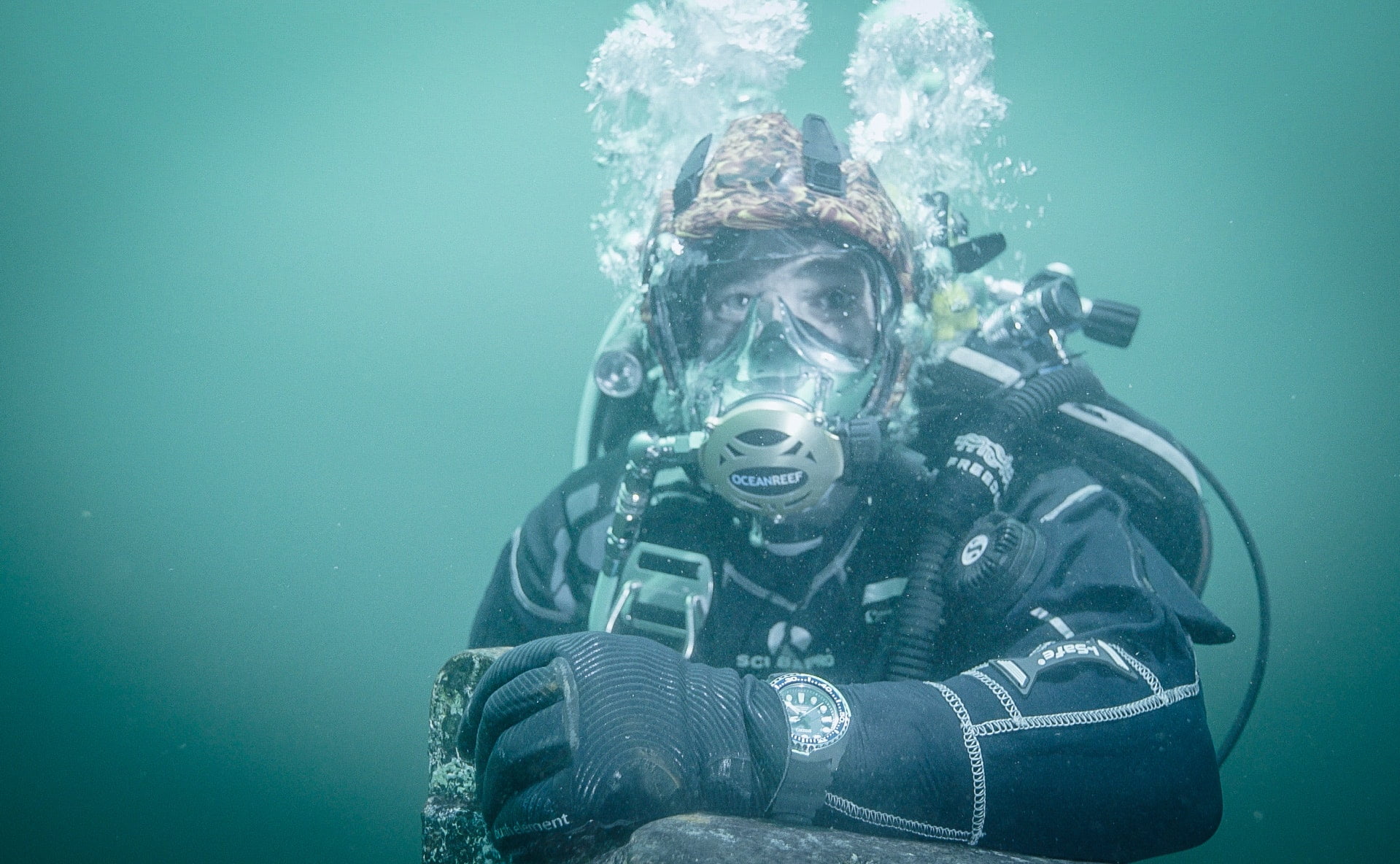
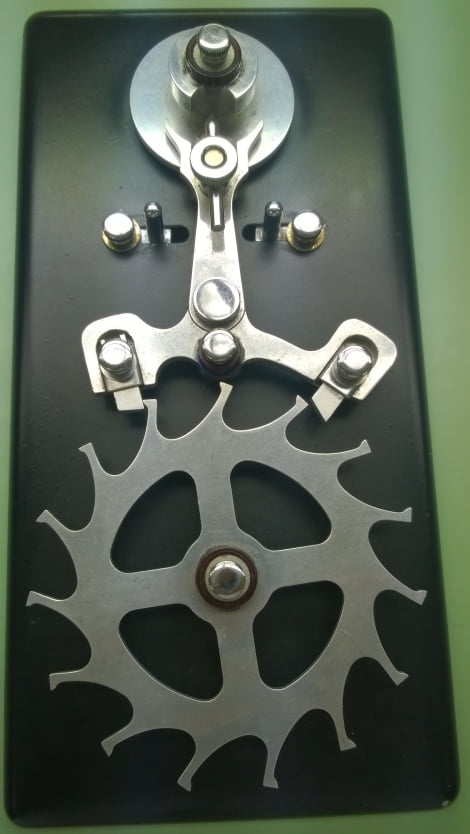
All FAE Wristwatches are water-restistant. But what does that mean? How does a watch resist water?
A watch is considered “water-resistant” when it is designed and constructed to withstand exposure to water to a certain extent. The water resistance of a watch is measured in units of pressure, typically expressed in meters, feet, or atmospheres (ATM).
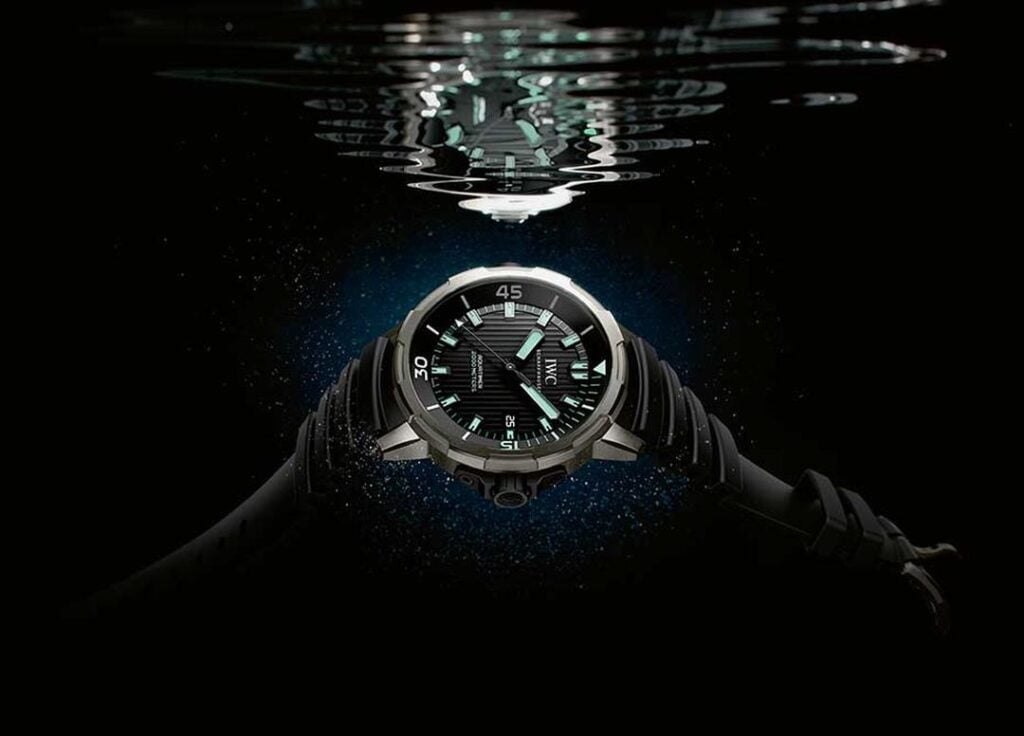

To make a watch water-resistant, several features and techniques are employed:
- Gaskets and Seals: The watch case, crystal, and crown (the knob used for setting the time) are fitted with gaskets or O-rings made of rubber or silicone. These gaskets create a watertight seal and prevent water from entering the watch.
- Screw-down Crown: Many water-resistant watches have a screw-down crown. When the crown is pushed in and screwed down tightly, it creates a seal that helps prevent water from penetrating the case.
- Case Design: Water-resistant watches typically have a sturdy and well-sealed case design. The case back is often screwed down or secured with a gasket to ensure water resistance.
- Crystal: The watch crystal, which covers the dial, can be made from various materials such as acrylic, mineral glass, or synthetic sapphire. Synthetic sapphire is highly scratch-resistant and offers excellent water resistance.
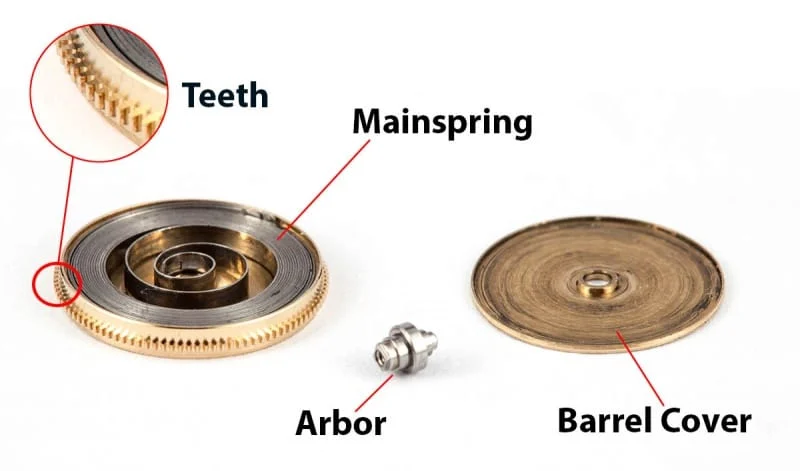
- Water-Resistant Movement: The watch movement itself may be designed with special seals and lubricants to protect it from moisture and water damage.

It’s important to note that water resistance is not a permanent feature of a watch and can deteriorate over time due to wear, aging of gaskets, or damage to the seals. Also, water resistance is tested under laboratory conditions and may not guarantee the watch’s performance in real-world situations, such as rapid temperature changes, extreme depths, or underwater activities.

Phone Consulation: 15 Minutes
Whether you need help picking a FAE Watch movement type, or help designing your custom, hand-made watch, whether you have questions about your grandfather’s broken watch, or need help with ideas for an anniversary or graduation presents, we are just a phone call away. Even if you are considering a major watch purchase, and would like a different perspective on its relative value, don’t be afrai…
Water-Resistance Rating
Manufacturers usually specify the water resistance rating of a watch, indicating the depth to which it can be safely submerged. Common water resistance ratings include:
- 30 meters (3 ATM or 100 feet): Suitable for everyday use, but not suitable for swimming or diving.
- 50 meters (5 ATM or 165 feet): Can be worn while swimming in shallow water.
- 100 meters (10 ATM or 330 feet): Suitable for recreational swimming and snorkeling.
- 200 meters (20 ATM or 660 feet): Suitable for recreational scuba diving.
- 300 meters (30 ATM or 990 feet) or higher: Suitable for professional diving and extreme water sports.
It’s important to check the watch’s water resistance rating and follow FAE guidelines to ensure your watch remains water-resistant. Of most importance, make sure to get your Annual Maintenance done on time, as this includes a new Case Back O-Ring Gasket which helps ensure long-term water-resistance.
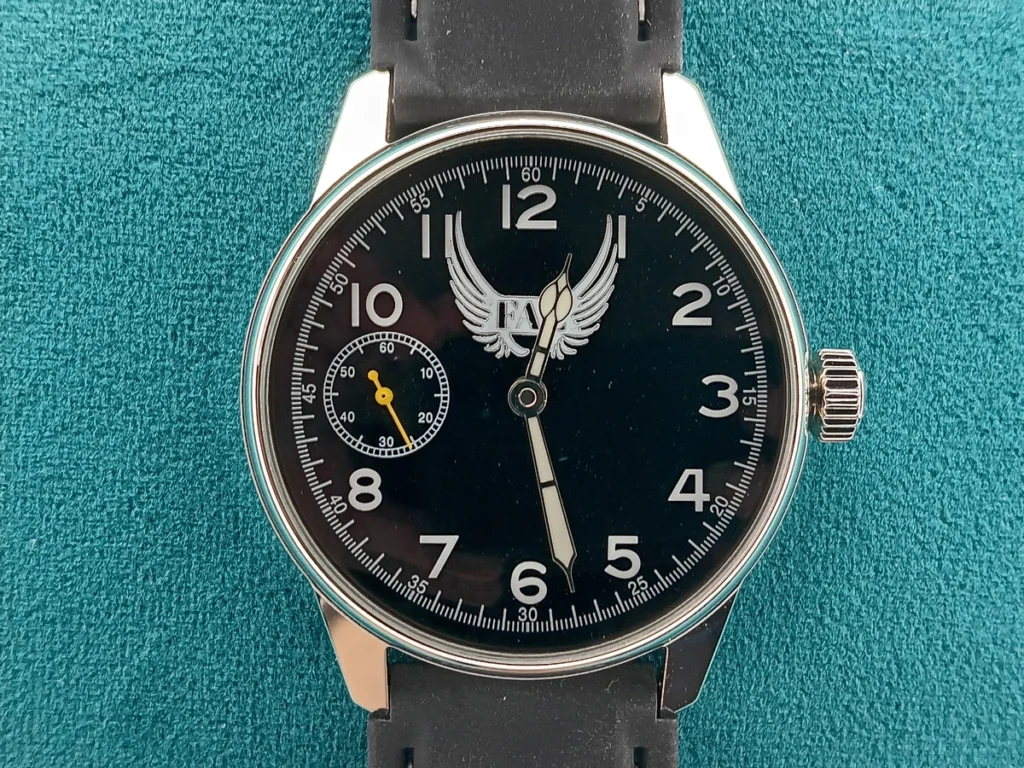

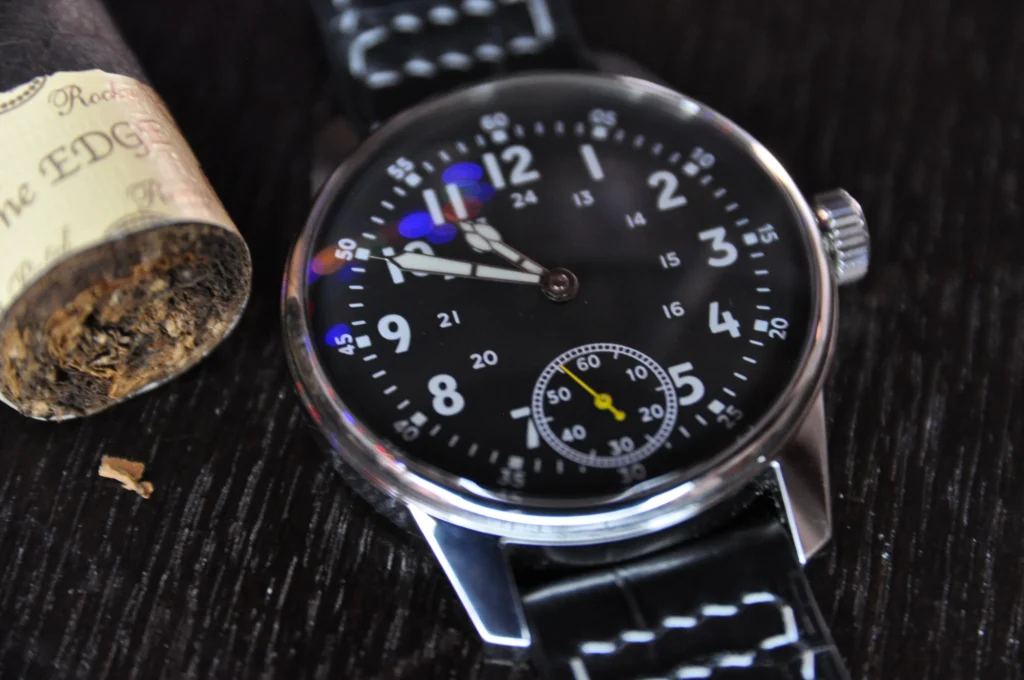
FAE Pilot Watch – Made in USA
[embedyt] https://www.youtube.com/embed?listType=playlist&list=PL0yjSttXSF0W445vM5Yv0fMiHMChkpONX&layout=gallery[/embedyt]For the pragmatic watch owner, the FAE Pilot Mechanical Watch. The Heartbeat of FAE.