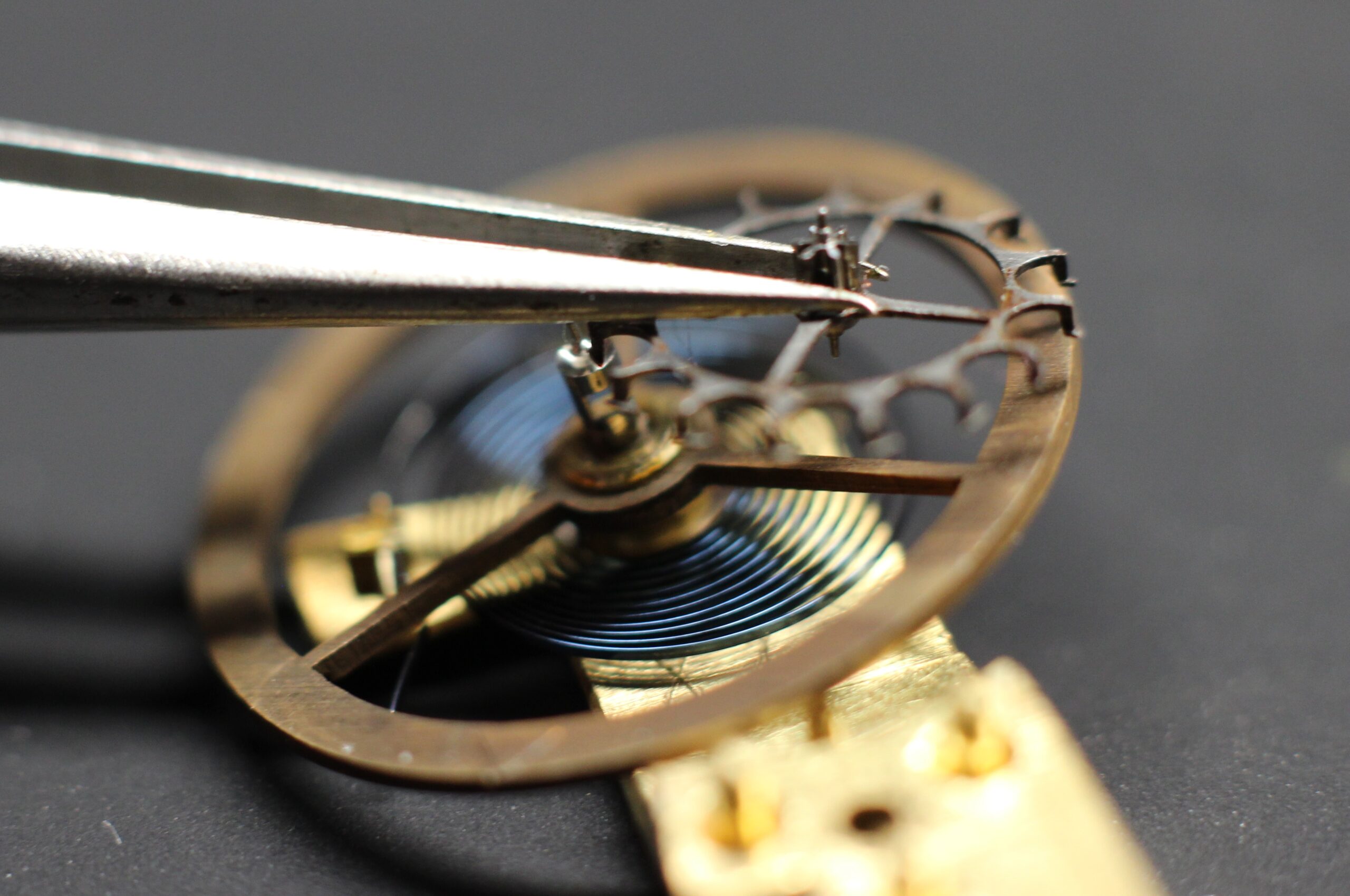
A watch escapement is a crucial mechanism in mechanical watches that regulates the release of energy from the mainspring and controls the movement of the watch’s hands. It consists of several components working together to ensure precise timekeeping. Here’s a simplified explanation of how a watch escapement works:
1. Mainspring: The mainspring is a coiled spring that stores potential energy when wound. As the mainspring unwinds, it releases this stored energy to power the watch.

2. Balance Wheel: The balance wheel is a wheel with a weighted rim that oscillates back and forth, creating a periodic motion. It acts as the timekeeping element of the watch, and its oscillations are what allow the watch to measure time.
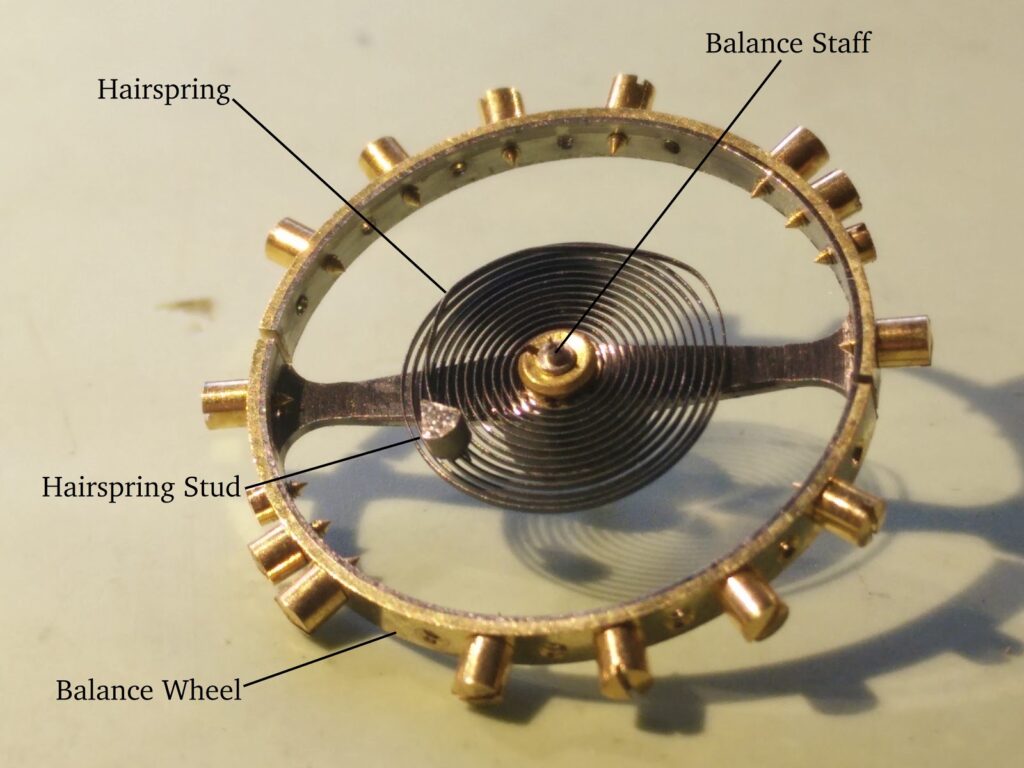
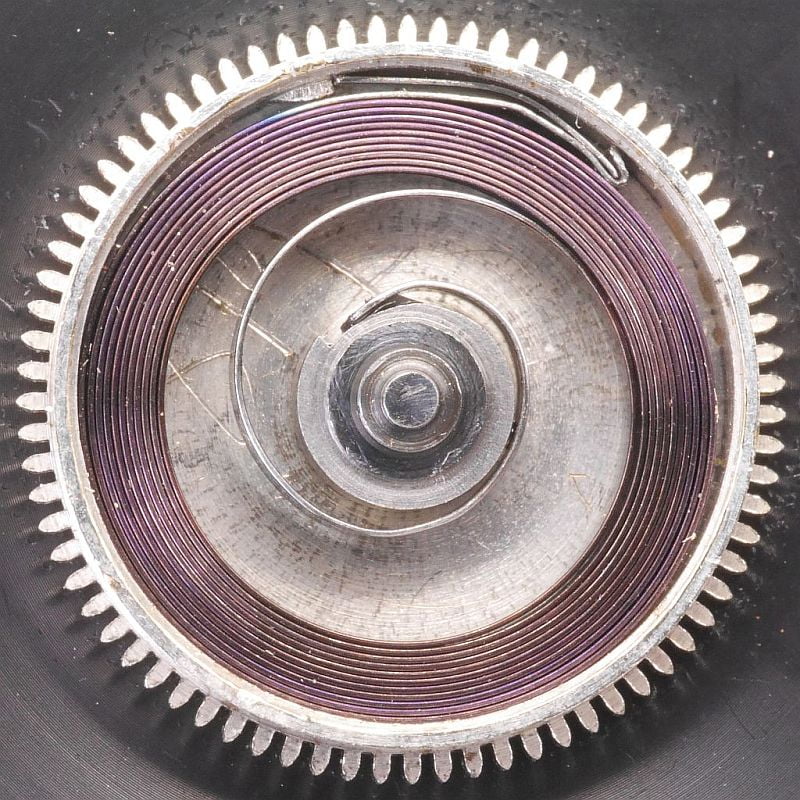
3. Balance Spring: The balance spring, also known as the hairspring, is a fine coiled spring attached to the balance wheel. It provides the restoring force that keeps the balance wheel oscillating back and forth at a consistent rate.
4. Escape Wheel: The escape wheel is a toothed wheel that interacts with the pallet fork to control the energy flow. It rotates in small increments, known as “ticks,” driven by the unwinding mainspring.
5. Pallet Fork: The pallet fork is a lever that engages with the escape wheel teeth. It has two small prongs, called pallet jewels, which alternately lock and unlock the escape wheel teeth, controlling the movement of the escape wheel.
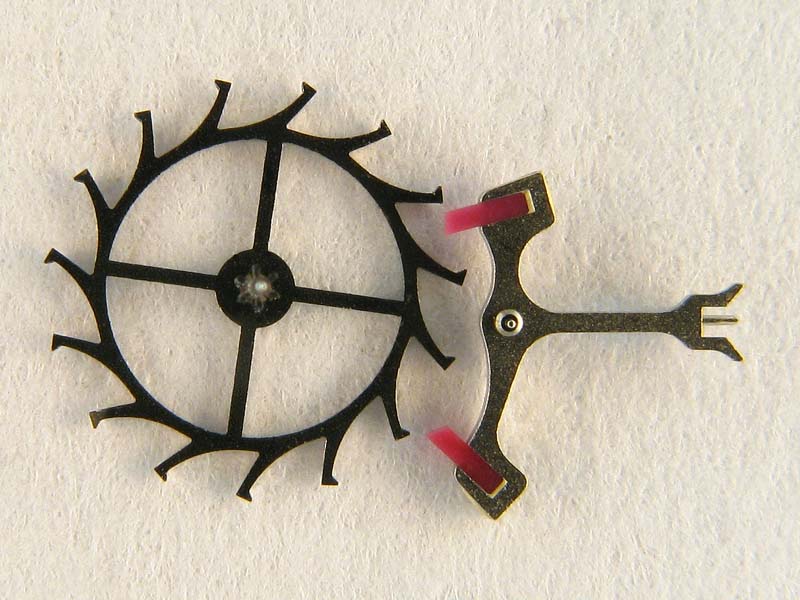
The interaction of the escape wheel and the pallet fork is the key to the escapement’s operation:
– Locking: As the balance wheel swings, the escape wheel rotates, and one of its teeth comes in contact with the pallet fork. This locks the escape wheel momentarily, stopping its rotation.
– Unlocking: The balance wheel continues its oscillation, causing the pallet fork to release the locked tooth of the escape wheel. The release of the tooth transfers a small amount of energy to the balance wheel, keeping it oscillating.
– Impulse: When the escape wheel tooth unlocks, the energy stored in the mainspring is transferred to the balance wheel, causing it to swing in the opposite direction. This transfer of energy is known as the “impulse,” and it maintains the oscillation of the balance wheel.
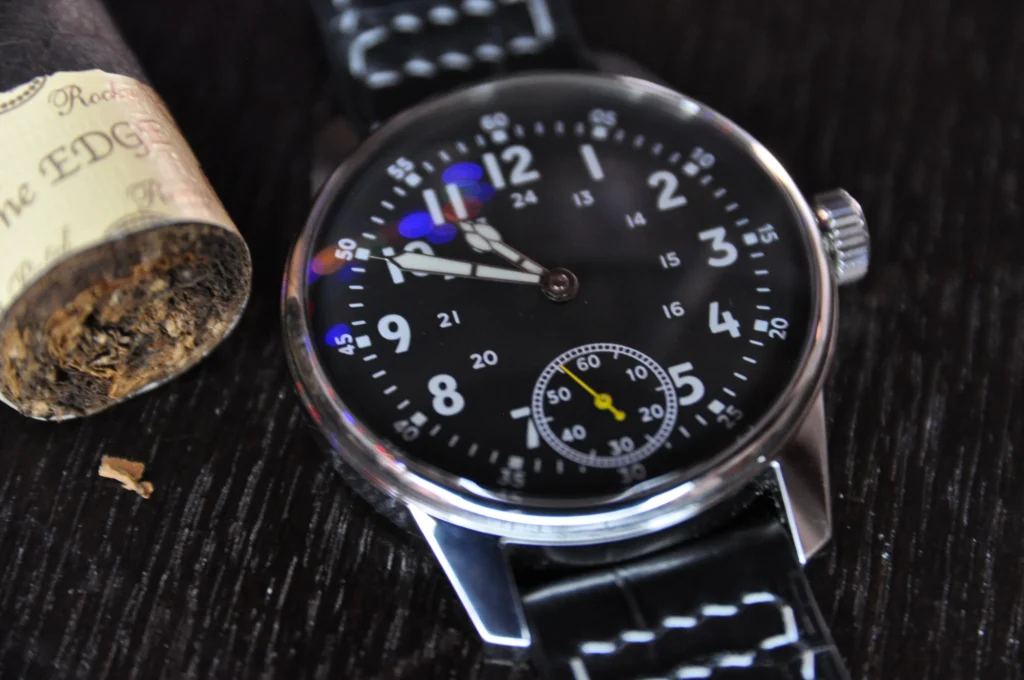

Custom FAE Mechanical Watch – Made in USA
For the pragmatic yet discerning watch owner, FAE offer the “Sapphire” edition of the Field Mechanical Watch which features all possible upgrades.
This process repeats with each swing of the balance wheel, creating a regular oscillation and precise timekeeping. The escapement effectively divides the unwinding of the mainspring into small, precise increments to ensure accurate timekeeping and control the speed of the watch’s movement.
It’s important to note that there are various types of escapements used in different watches, including the lever escapement, Swiss lever escapement, and co-axial escapement, among others. Each type has its own design and characteristics, but the fundamental principle of regulating energy flow remains similar across all escapements.
[…] train consists of a series of gears that transfer the rotational energy from the mainspring to the escapement mechanism. The escapement regulates the release of this energy in precise increments, enabling the […]